Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


The mucosal immune complex paired with salicylates provides substantial relief from common cold symptoms, such as sore throat pain and congestion.
A study published in “PLOS One” found that throat spray formulated with a mucosal immune complex (MIC) (made of lysozyme, lactoferrin, and aloe) and anti-inflammatory salicylates can markedly reduce symptoms of common cold. The study, involving 157 participants (aged 21-66 years), sought to assess whether MIC + anti-inflammatory salicylates can enhance the efficacy of aspirin (cyclooxygenase [COX]-enzyme inhibitor) in easing common cold symptoms.
Participants with common cold symptoms lasting less than 2 days were randomly assigned to:
Participants administered their own treatments—throat sprays every hour and tablets every 4 hours—and filled out surveys from the comfort of their homes over a span of 2 days. The key outcomes were:
Both the primary and secondary endpoints were achieved. Sore throat pain, assessed by STPIS, showed a 68-75% reduction by 36 hours, depending on the treatment. Other symptoms, including cough, congestion, malaise, nasal discharge, sneezing, and sore throat, as estimated by MJS, decreased by 38-68%, depending on the type of treatment. In the repeated measures analysis, all the treatments prominently reduced sore throat pain and cold symptom severity from baseline to 36 hours and from days 1 to 2. Treatment groups showed notable improvements, with treatment 3 yielding the greatest reduction in both sore throat pain and cold symptoms (Table 1).
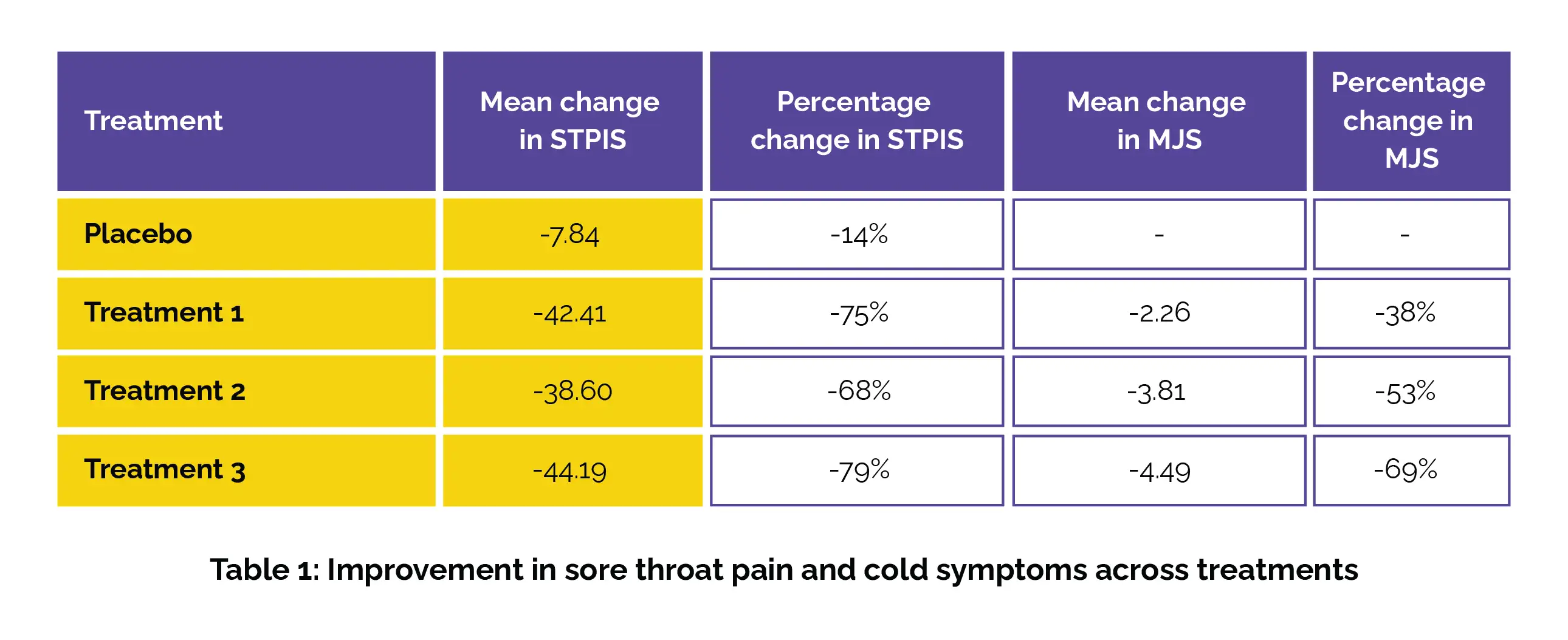
The findings suggest that supporting upper respiratory epithelia and decreasing COX-mediated inflammation may be a valuable strategy for treating common cold symptoms, potentially offering a promising alternative to traditional over-the-counter cold medications.
PLOS One
Supporting respiratory epithelia and lowering inflammation to effectively treat common cold symptoms: A randomized controlled trial
Pavel Pugach et al.
Comments (0)