Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Integrating pharmacotherapy, environmental interventions, and behavioural therapy is key to multimodal therapy, enabling more effective and personalized AR treatment.
A recent trial published in the “European Journal of Medical Research” found significant advantages of multimodal therapy in managing allergic rhinitis (AR) symptoms and enhancing patients' quality of life.
To assess the efficacy of a multimodal or comprehensive therapy regimen for AR, Yafang Yu and Jianwen Yan included a hundred patients with AR. They were allocated to the intervention group (patients subjected to multimodal therapy) or the control group (usual treatment). With 50 participants in each group, the study employed standardized AR questionnaires to gauge symptom severity, focusing on relief times and overall treatment efficacy.
The results were striking: patients in the multimodal therapy group experienced suggestively quicker symptom relief across numerous key AR symptoms. Also, itching in the nose, congestion, rhinorrhea, and sneezing were significantly relieved much faster than in the control group (Table 1).
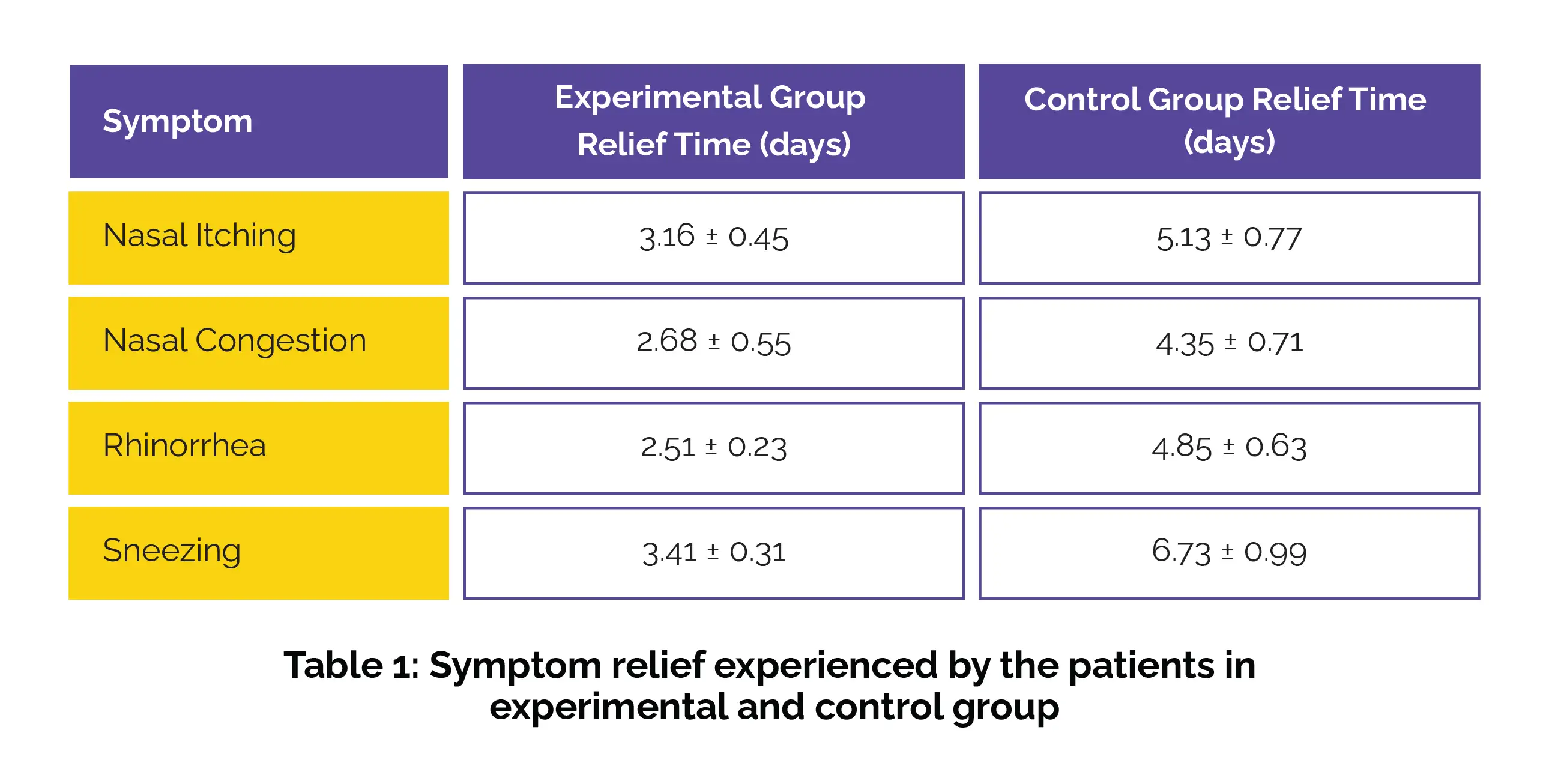
Compared to the control group (66%), the intervention group showed significantly higher treatment effectiveness, with a 90.0% success rate. Summing up, multimodal therapy offered rapid symptom relief and improved well-being, marking a key advancement in AR treatment.
European Journal of Medical Research
Effectiveness of a multimodal therapy protocol for the management of allergic rhinitis: a randomized controlled trial
Yafang Yu, Jianwen Yan
Comments (0)