Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Assessment of serum arginine and nitric oxide levels might aid clinicians in diagnosing individuals with seasonal allergic rhinitis who are difficult to diagnose.
In seasonal allergic rhinitis patients, L-arginine levels declined while the levels of Nitric oxide (NO) raised when compared to healthy controls, as deciphered from a recent study. Nihal Efe Atila et al. aimed to examine the processes involved in the etiopathogenesis of rhinitis and whether amino acids are useful in the development of seasonal allergic rhinitis. Furthermore, the authors explored the presence of a modification by comparing serum-free amino acid levels between healthy controls and allergic rhinitis people.
The research group (Group 1) included 44 people with seasonal allergic rhinitis, while the control group (Group 2) included 33 healthy subjects. According to the allergy-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibody test (the inhalant allergen test), patients in Group 1 had increased specific IgE antibodies against minimum one of the following: mite, mold spores, grass, or tree. Patients had minimum 1 allergic rhinitis symptoms and had the condition for at least 2 years. The levels of 25 serum-free amino acids were assessed in both groups using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) equipment.
In both groups, the griess reaction was used to assess the levels of serum NO. Nitrite and nitrate concentrations were utilized as indicators for measuring NO. In comparison to Group 2, the serum-free L-arginine level of Group 1 was shown to be considerably lower. Additionally, there was a discernible rise in NO levels in Group 1 compared to Group 2 (Table 1).
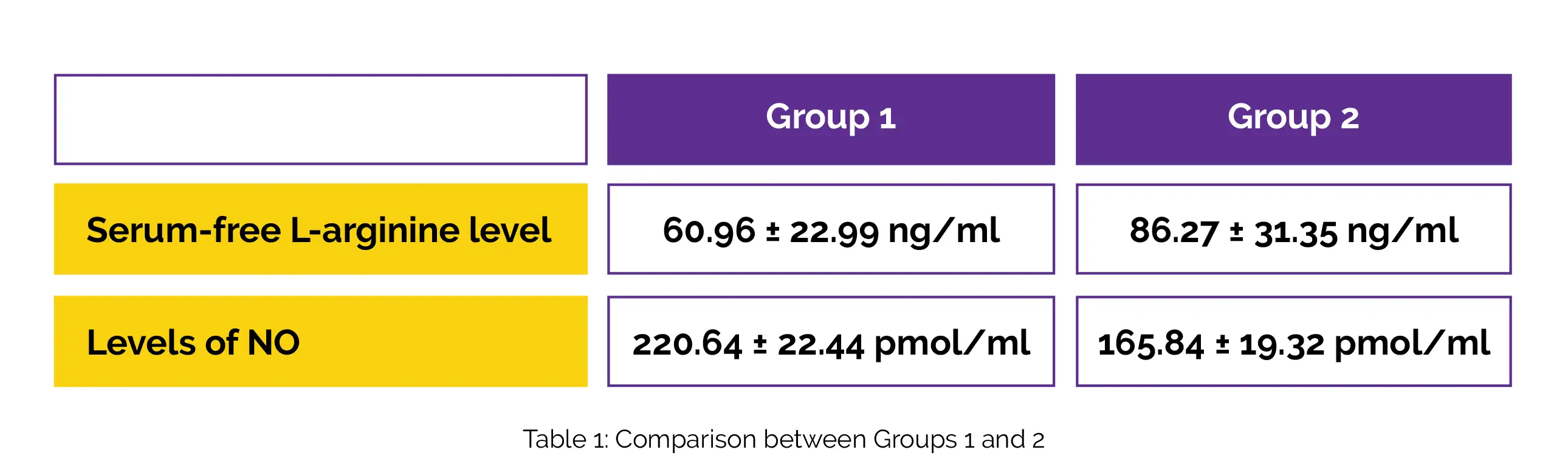
Hence, the examination of the physiopathology of seasonal allergic rhinitis and potential therapeutic strategies should take into account the arginine/NO balance.
The Injector
Does the balance of Nitric oxide and L-arginine play a role in the development of allergic rhinitis?
Exploratory, Diagnostic, Nitric oxide, L-arginine, Allergic rhinitis, ENT, Otorhinolaryngology, Allergology
Comments (0)