Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Ivermectin showed a statistically significant and dose-dependent effect to reduce the time to SARS-CoV-2 negativity in people with mild to moderate COVID-19.
A recent proof of concept study published in "QJM: An International Journal Of Medicine" revealed a likely beneficial therapeutic effect of ivermectin to decrease the duration of illness, trigger prompt recovery and diminution of qualitative indices of viral load in comparison with the usual treatment in COVID-19 people with RT-PCR proven SARS-CoV-2 positivity.
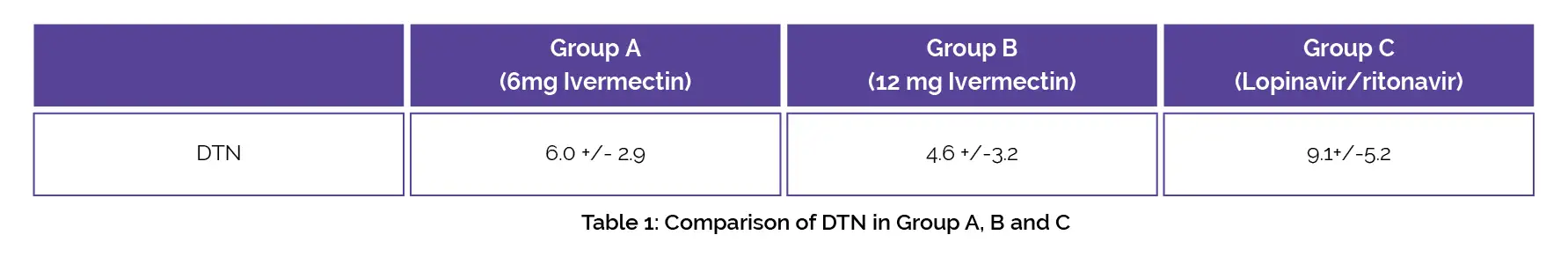
This randomized controlled trial was performed to assess the safety and effectiveness of ivermectin for COVID-19 management. A total of 62 subjects with mild to moderate COVID-19 symptoms were randomly segregated into 3 groups. Group A was given 6 mg ivermectin every 84 hours twice a week, Group B was given 12 mg ivermectin every 84 hours for two weeks and Group C was given lopinavir/ritonavir every day for two weeks + placebo.
The primary endpoints were: (i) Number of Days-to-Negative (DTN) of the PCR test, and (ii) Therapy effect assessed via two-way Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance (RAMOVA). The alteration in liver function tests (LFT), rheological variables such as platelet count and prothrombin time, SPO2, clinical status, kidney function tests (KFT) were secondary endpoints ascertained.
The DTN was profoundly and dose-dependently decreased by ivermectin as shown in Table 1.
In comparison with Group C, ivermectin therapy increased the SPO2% and platelet count in Group A and Group B. The rise in the platelet count was inversely related to DTN. At 0, 84, 168, 232 hours, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA of ranked coronavirus + / - scores illustrated a considerable ivermectin time effect and therapeutic effect. No serious side effects were recorded.
Hence, administration of 12 mg ivermectin therapy twice a week might exhibit superior effectiveness over 6 mg ivermectin administered twice a week, and definitely over the non-ivermectin group. Ivermectin should be used in the clinical management of coronavirus infections, and in high-risk areas, it may be used for community prophylaxis.
QJM: An International Journal of Medicine
Ivermectin shows clinical benefits in mild to moderate COVID19: a randomized controlled double-blind, dose-response study in Lagos
O E Babalola et al.
Comments (0)