Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In modified osteotomy technique, intravenous administration of Tranexamic acid may be an efficient and safe measure for controlling perioperative hemorrhage in patients with varus knee osteoarthritis.
Intravenous use of Tranexamic acid during medial opening-wedge distal tibial tuberosity osteotomy (MOWDTO) decreased perioperative blood loss without raising the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), according to a recent trial. Researchers wanted to know if patients (older than twenty years) with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis scheduled to undergo MOWDTO would experience less perioperative blood loss after receiving injectable Tranexamic acid.
In this randomized control study, 61 knees in 59 participants who underwent MOWDTO during the study period were arbitrarily allocated to either the Tranexamic acid group (intravenous Tranexamic acid group) or the control group (no Tranexamic acid administration). Patients in the Tranexamic acid group received 1000 mg of Tranexamic acid intravenously six hours prior to making a skin cut. The major endpoint, which was determined using the hemoglobin decline and blood volume was the amount of perioperative total blood loss.
The disparity between preoperative and postoperative hemoglobin levels at days 1, 3, and 7 were used to determine the hemoglobin decline. The subjects in the Tranexamic acid group experienced substantially less perioperative total blood loss (543 ± 219 ml vs. 880 ± 268 ml). The hemoglobin decline was markedly less in the Tranexamic acid group than in the control group on postoperative days 1, 3, and 7, as shown in Table 1:
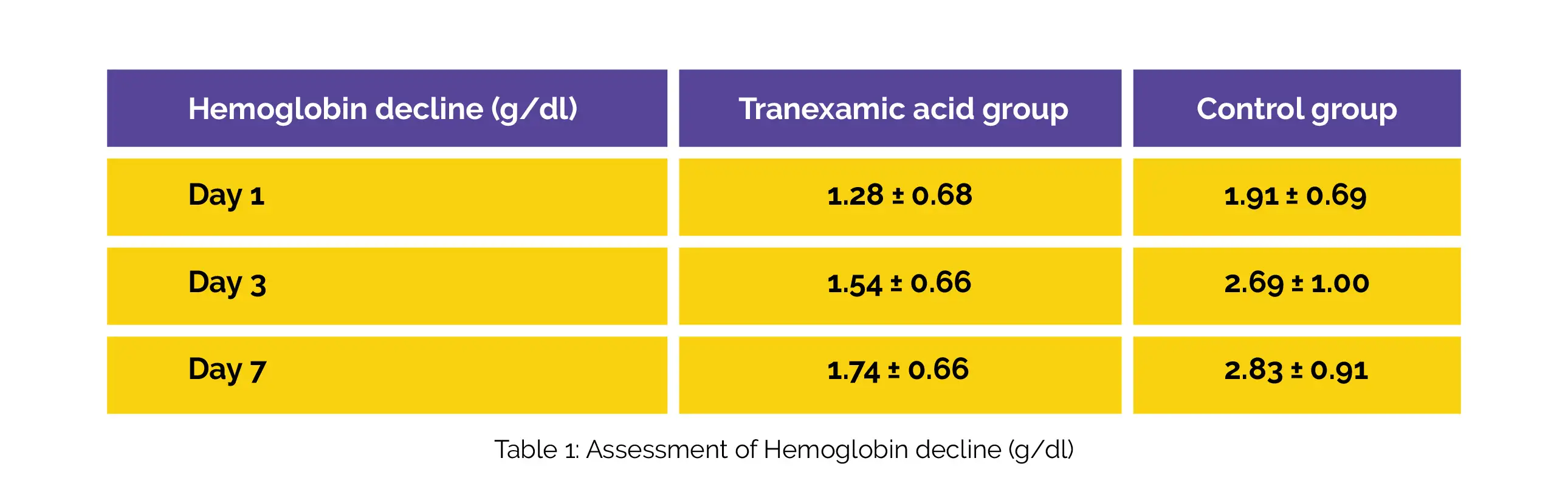
Thus, administration of intravenous Tranexamic acid in MOWDTO is beneficial to lessen perioperative blood loss.
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research
Efficacy of intravenous Tranexamic acid administration in medial opening-wedge distal tibial tuberosity osteotomy (MOWDTO) for varus knee osteoarthritis: a randomized control trial
Takuya Iseki et al.
Comments (0)