Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In patients scheduled to undergo removal of impacted mandibular third molars, the intra-socket use of hyaluronic acid decreases postoperative pain and swelling.
A prospective, randomized, split-mouth clinical trial published in The Journal of Oral Medicine and Oral Surgery depicted that the application of intra-socket hyaluronic acid solution exerts a positive effect on reduction of postoperative pain, swelling, and trismus following the lower third molar intervention. Researchers sought to investigate the efficacy of hyaluronic acid (0.7 ml from 20 mg/2 ml solution) to minimize the uncomfortable post-operative events such as pain, edema, and limited mouth opening in 30 people who underwent dental surgery.
In this cross over and double-blind trial, an intra-socket application of hyaluronic acid solution with gel foam as a scaffold in the study site vs gel foam only on the control site was carried out. During the pre-operative period and on the post-operative 2nd and 7th day, recording of the data collection of five facial reference points for swelling and maximum mouth opening was done.
The number of analgesic consumption for the 7-day postsurgery duration and the visual analog scale (VAS) pain score on postoperative days 1, 2, and 3 were investigated. The hyaluronic acid group displayed remarkably reduced swelling, trismus and analgesia consumption on the 2nd and 7th day following dental surgery. In comparison with the control group, the hyaluronic acid group illustrated considerably decreased VAS scores on days 1, 2 and 3 following wisdom teeth removal, as shown in Table 1:
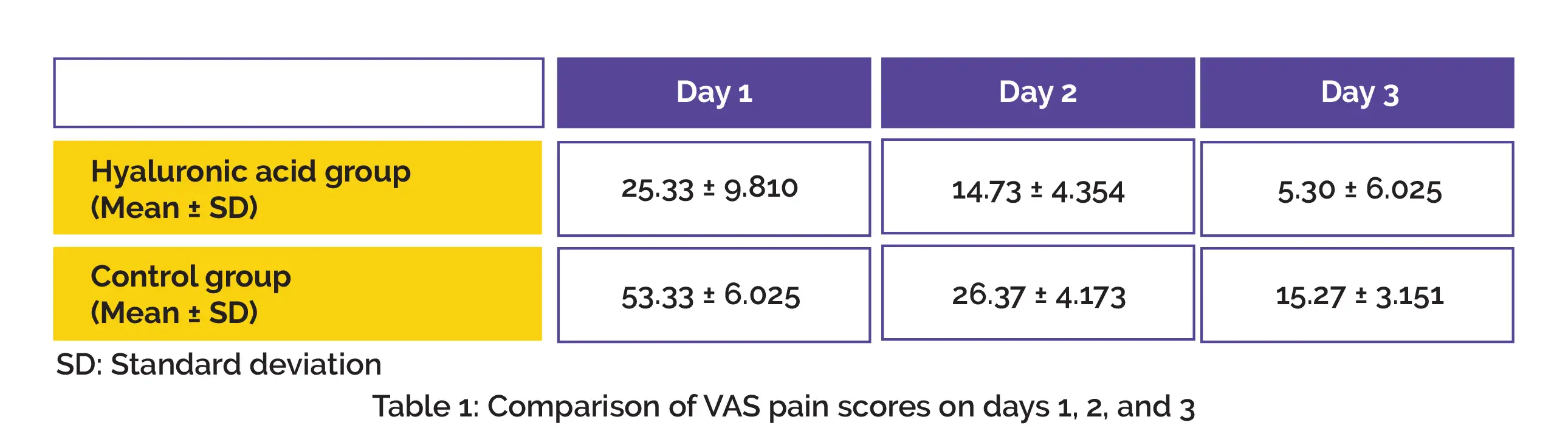
Thus, the use of the intra-socket hyaluronic acid solution is a promising strategy to alleviate pain and trismus from edema, and also reduce the use of painkillers after bilateral extractions of mandibular wisdom teeth.
Journal of Oral Medicine and Oral Surgery
Intra-socket application of Hyaluronic acid reduces pain and swelling following wisdom teeth removal
Nadia Sultana Shuborna et al.
Comments (0)