Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In individuals diagnosed with episodic migraine, 120 mg Galcanezumab given once monthly effectively reduced the overall mean number of monthly migraine headache days over the 3-month treatment period.
A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled research (PERSIST) depicted that patients with episodic migraine responded well to 120 mg Galcanezumab and it was both efficacious and well-tolerated. Bo hu et al. aimed to evaluate Galcanezumab's safety and effectiveness in treating episodic migraine. During the double-blind, three-month treatment, adults suffering from episodic migraine were randomly segregated in a 1:1 ratio to get administered with either 120 mg Galcanezumab (with a 240 mg loading dose) or placebo, monthly.
From baseline, the overall mean change in monthly migraine headache days (MHDs) served as major outcome. Mean alteration in Migraine-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire (MSQ) Role Function-Restrictive domain score and the mean proportion of people with MHD reductions of ≥ 50%, ≥ 75%, and 100% from baseline were crucial secondary outcomes. Overall, 520 patients were assigned to one of two groups: Galcanezumab (n = 261) or placebo (n = 259). Least squares mean decrease from baseline in monthly MHDs with Galcanezumab was considerably higher compared to placebo over three months.
Galcanezumab patients exhibited substantially higher mean percentage of MHD reductions of ≥ 50%, ≥ 75%, and 100% from baseline compared to placebo patients. In the MSQ Role Function-Restrictive score, Galcanezumab considerably outperformed the placebo in terms of overall mean improvement from baseline over the course of 3 months. Except for a greater occurrence of injection site discomfort, injection site reaction, and injection site pruritus, there were no statistically significant differences in any safety variables between the Galcanezumab and placebo groups, as depicted in Table 1:
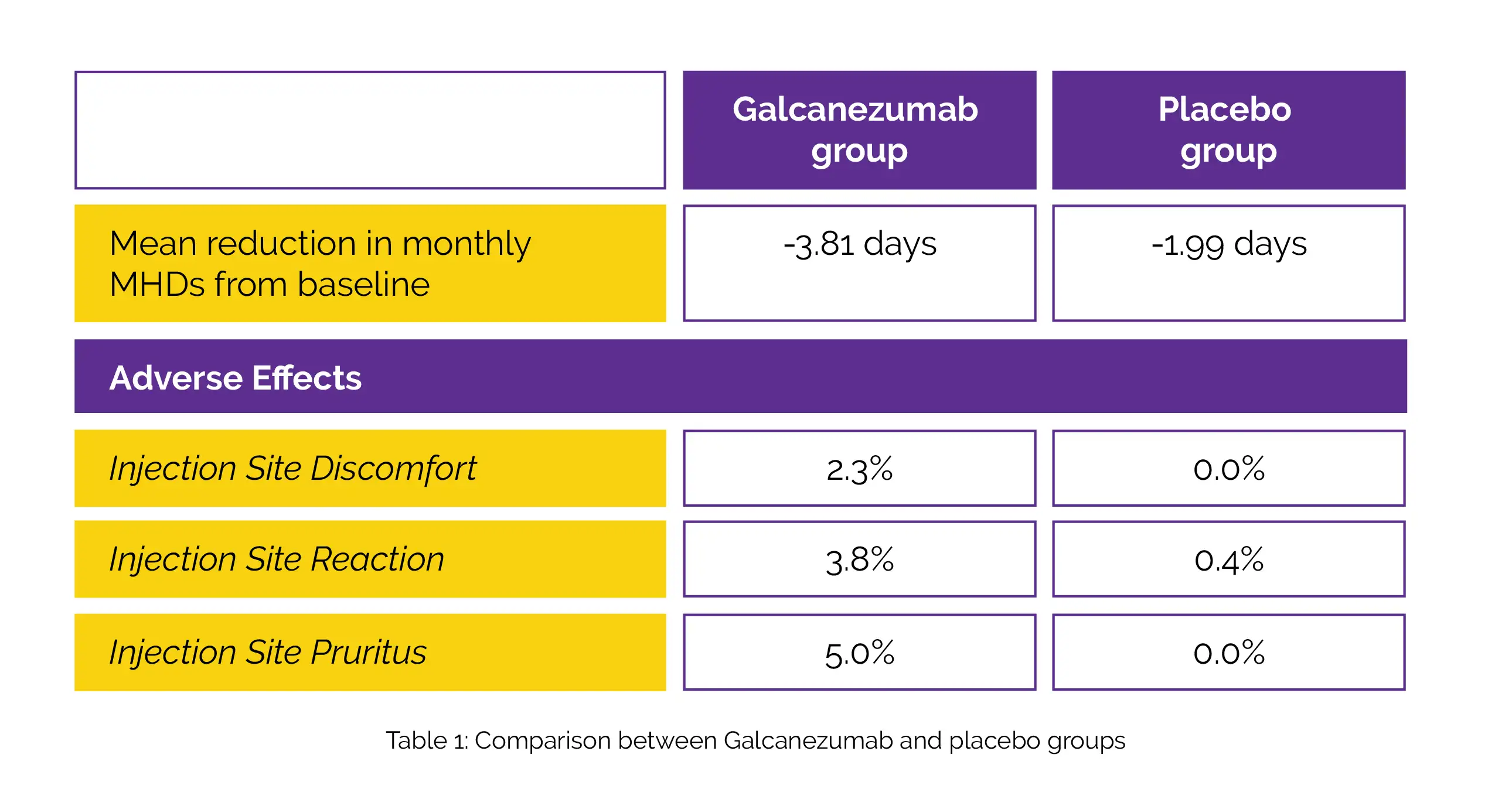
Except for one patient who experienced a significant injection site reaction, TEAEs linked to injection sites were mildly severe. Notably, six patients reported 6 severe side effects (2 Galcanezumab, and 4 placebo). In terms of primary and secondary endpoints, the humanized monoclonal antibody Galcanezumab was substantially more effective than the placebo.
Journal of Headache and Pain
Galcanezumab in episodic migraine: the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled PERSIST study
Bo Hu et al.
Comments (0)