Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In patients with diabetic neuropathy, Duloxetine is more efficient than Amitriptyline, particularly in lowering the number of times patients experience pain.
According to the outcomes of a randomized controlled trial, Duloxetine was more effective than Amitriptyline, particularly in reducing the number of times patients reported feeling discomfort. Salman Azhar et al. compared the pain-relieving benefits of Amitriptyline and Duloxetine in diabetic neuropathy. Overall, 150 subjects suffering from diabetic neuropathy were recruited and randomized equally into Group A and Group B. Subjects in Group A were administered Duloxetine (60 mg) while those in Group B were given Amitriptyline (75 mg) for six weeks.
A diary card was employed during patient consultations. For the first 3 weeks, patients tracked daily progress on a visual analogue scale (VAS). Three weeks of medication were given, and a 6-week assessment was scheduled. Pain levels were classified as "reduced" when they were 50% lower than their initial values. The subjects were followed up via phone.
Forty-one (54.67%) subjects in Group A and thirty-nine (52%) subjects in Group B were men. Thirty-four (45.33%) subjects in Group A and thirty-six (48%) subjects in Group B were women. Notably, 46.19+6.39 years was the mean age of the participants. In terms of mean VAS pain ratings, no clinically meaningful difference was noted between both groups at baseline. Following six weeks of therapy, a statistically significant inter-group difference was reported, as depicted in Table 1:
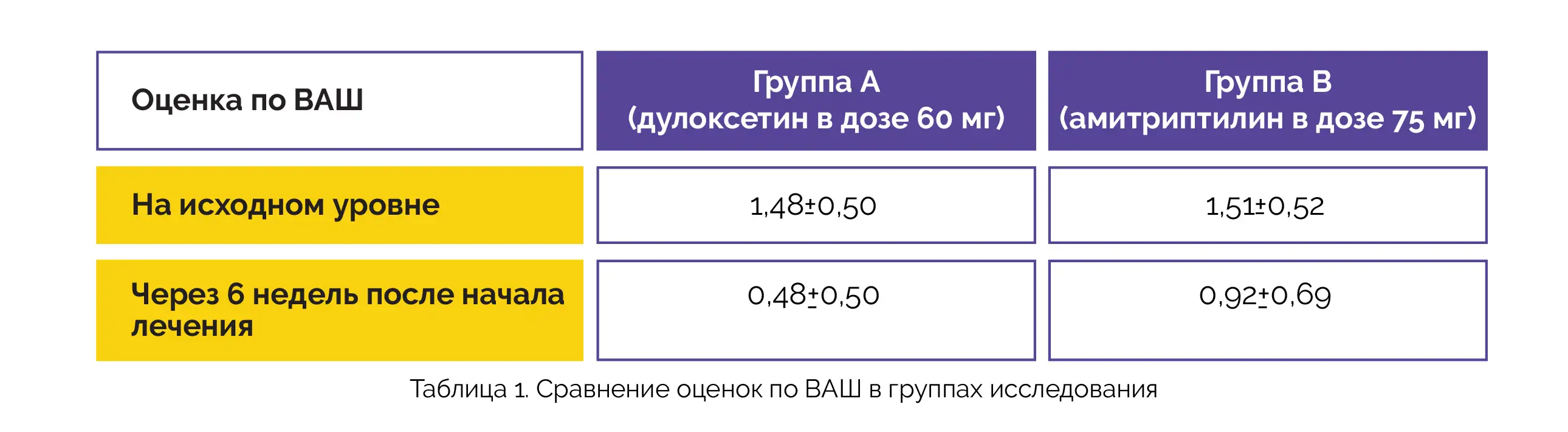
Hence, Duloxetine exhibits better pain-relieving effects than Amitriptyline in diabetic neuropathy-affected people.
Pakistan Journal of Medical & Health Sciences
Management of Diabetic Neuropathy: A Comparison of Duloxetine with Amitriptyline
Salman Azhar et al.
Comments (0)