Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


During cesarean section, quadratus lumborum block using bupivacaine along with dexmedetomidine prolongs analgesia in the absence of intrathecal morphine.
In a randomized controlled study, dexmedetomidine was proven to be successful add-on therapy in ultrasound-guided quadratus lumborum block (QLB) in patients having cesarean section. Researchers sought to assess dexmedetomidine's effect as an adjuvant in QLB for postoperative pain mitigation at rest in women undergoing cesarean section.
In this double-blind study, the major target was to compare the period from the initial request for rescue analgesia. Secondary targets included comparing the quantity of rescue analgesia, patient satisfaction, the numeric rating scale (NRS), and the Ramsay sedation score (RSS) over the first 24 hours. Over 70 women with singleton pregnancies scheduled for cesarean under spinal anesthesia were incorporated in the study.
In the recovery area, bilateral QLB was administered. Group A was given 30 ml of 0.25 percent bupivacaine, whereas Group B was given 30 ml of 0.25 percent bupivacaine with 1 µg/kg dexmedetomidine. They were administered an intravenous TDS (three times daily) injection of 15 mg/kg paracetamol and 1 mg/kg tramadol injection as rescue analgesia (if their NRS score was >4).
Comparison was done of rescue analgesia in initial 24 hours, and patient satisfaction scores, NRS, and RSS scores at 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 18, and 24 hours. In group B, it took a much longer time to request rescue analgesia than in group A. Compared to Group A, a considerable drop in the amount of rescue analgesia [Injection tramadol (1 mg/ kg)] used was noted in group B, as shown in Table 1:
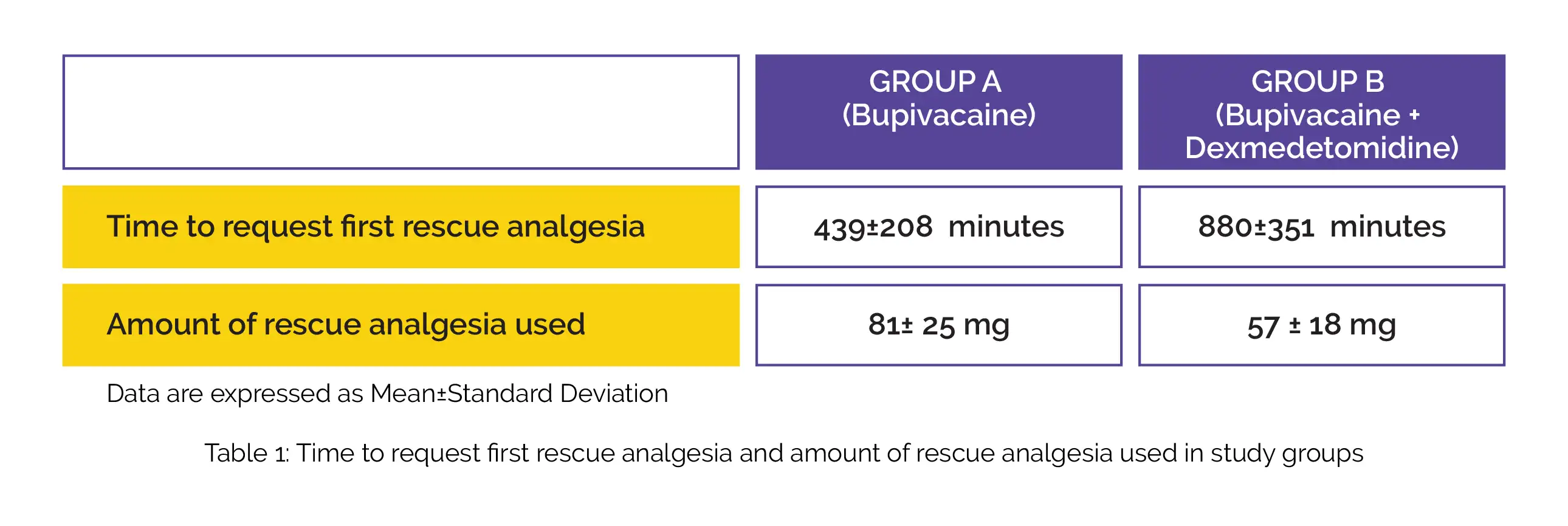
A profound difference was noted in patient satisfaction scores and pain scores between the study groups up to 18 hours but not in RSS. In the absence of intrathecal morphine, dexmedetomidine can be therefore regarded as an effective adjuvant for QLB in cesarean section with reduced rescue analgesic amount and higher patient satisfaction scores up to 18 hours after surgery.
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia
Effect of Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant in quadratus lumborum block in patient undergoing caesarean section – A randomised controlled study
Neha Singh et al.
Comments (0)