Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Post-neurotomy administration of dexamethasone is beneficial to lower the occurrence of neuropathic pain.
In people undergoing lumbar, cervical, thoracic, or sacroiliac joint radiofrequency neurotomy, dexamethasone (a corticosteroid) use led to remarkable improvements in post-neurotomy neuropathic pain. Alexander Shustorovich et al. undertook this study to explore dexamethasone's effectiveness to prevent the development of neuropathic pain after radiofrequency denervation.
The study recruited people having joint pain and positive concordant medial branch blocks (therefore scheduled to undergo bilateral radiofrequency neurotomy). In this randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled, double-blind pilot study, participants were given dexamethasone versus normal saline (control group) at each lesion site, acting as their own control (with laterality). After 4 and 8 weeks of treatment, the participants were followed up.
With the aid of Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) or Neck Disability Index (NDI), the postoperative function was evaluated. Using a questionnaire, the occurrence of post-procedure pain was evaluated. At the time of data assessment, the study protocol was finished by 35/63 people. Compared to the control group, the steroid group exhibited diminished incidence of post-neurotomy neuropathic pain, as shown in Table 1:
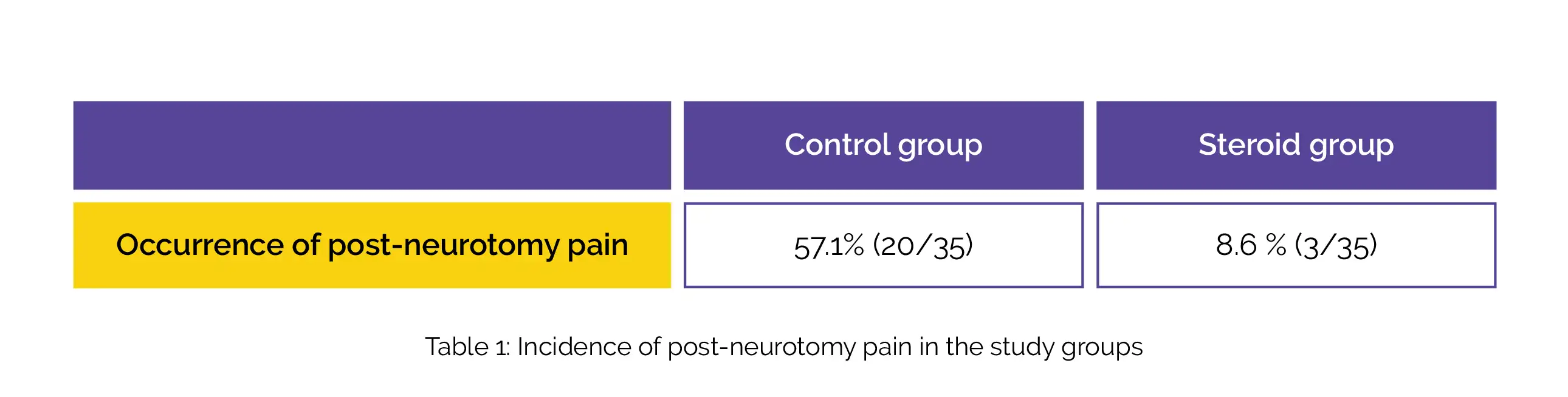
Based on the spinal level of neurotomy, the ODI/NDI scores altered differently over time. After four and eight weeks, remarkable improvements were noted in the ODI/NDI in the cervical subgroup and lumbar subgroup respectively. In the sacral subgroup, no improvement in ODI scores was noted.
In people having distinct spinal levels of neurotomy, the occurrence of post-neurotomy neuropathic pain was not considerably distinct. People who developed post-neurotomy neuropathic pain were not different in terms of ODI/NDI scores. Thus, dexamethasone minimizes the risk of neuropathic pain after radiofrequency neurotomy.
Pain Physician
Dexamethasone Effectively Reduces the Incidence of Post-neurotomy Neuropathic Pain: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Alexander Shustorovich et al.
Comments (0)