Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


Combining Dexamethasone with Bupivacaine in transincisional paravertebral block extends pain relief and lowers opioid use in lumbar spine surgeries.
A randomized controlled trial depicted that Dexamethasone added to Bupivacaine in transincisional paravertebral block (TiPVB) for lumbar spine surgeries improves pain relief, minimizes opioid consumption, and displays comparable adverse event rates when compared to Bupivacaine alone. Investigators aimed to compare the effectiveness of Dexamethasone plus Bupivacaine against the use of Bupivacaine alone in bilateral TiPVB for postoperative pain management in lumbar spine surgeries.
Overall, 50 participants (20-60 years of age), with American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status (ASA-PS) I or II, were randomized to two groups equally. Both groups underwent combined bilateral lumbar TiPVB and general anesthesia. In the Dexamethasone group (group 1, n=25), subjects were given 14 mL of Bupivacaine 0.20% along with 1 mL containing 4 mg of Dexamethasone on each side. In the control group (group 2, n=25), patients were administered 14 mL of Bupivacaine 0.20% and 1 mL of saline on each side.
The major endpoint was the time to first analgesic need, while secondary endpoints incorporated the occurrence of side effects, the visual analog scale (VAS) for pain assessment (ranging from 0 to 10), and total opioid consumption within the initial 24 hours post-surgery. Patients in the Dexamethasone-treated group experienced a significantly longer mean time until their first need for analgesics compared to those in the control group (Table 1).
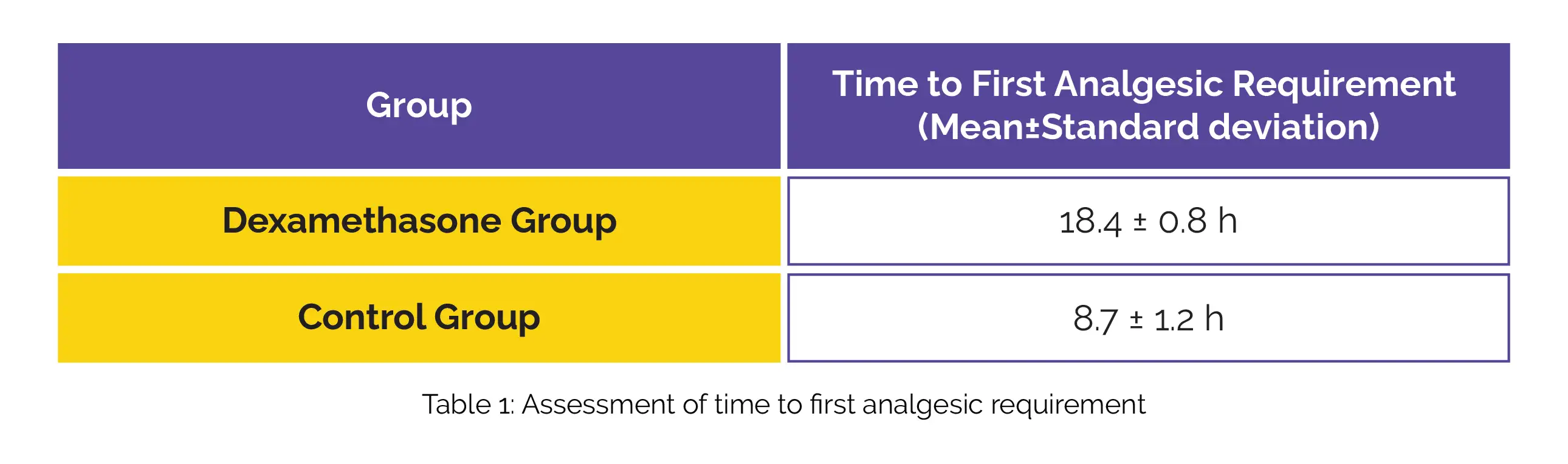
The Dexamethasone group also exhibited reduced overall opioid consumption compared to the control group. Although not statistically significant, instances of postoperative nausea and vomiting were more prevalent in the control group. In conclusion, the utilization of Dexamethasone in conjunction with Bupivacaine for TiPVB demonstrated promising outcomes in terms of favorably extending the pain-free interval and diminishing opioid consumption in lumbar spine surgeries.
The Clinical Journal of Pain
Dexamethasone Plus Bupivacaine Versus Bupivacaine in Bilateral Trans-incisional Paravertebral Block in Lumbar Spine Surgeries, a Randomized Controlled Trial
Amin M. Alansary et al.
Comments (0)