Categories
Change Password!
Reset Password!


In patients having NASH or NAFLD (with or without diabetes), AZD4017 blocked conversion of 13 C cortisone to 13C cortisol in the liver.
In individuals suffering from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), either with or without type 2 diabetes, a twelve weeks of treatment with AZD4017 (a selective 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 [11β-HSD1] inhibitor) blocked the conversion of 13 C cortisone to 13C cortisol in the liver. In people with NASH and type 2 diabetes, AZD4017 led to improvements in liver steatosis, as elucidated from a phase II, randomized study.
Investigators sought to find out if short-term treatment with AZD4017 would impair hepatic cortisol production and thus reduce hepatic fat in NAFLD/NASH people. In this placebo-controlled, double-blind, proof-of-concept study, the volunteers (n=93) were randomly allocated to receive either AZD4017 (n=46) or placebo (n=47) for twelve weeks.
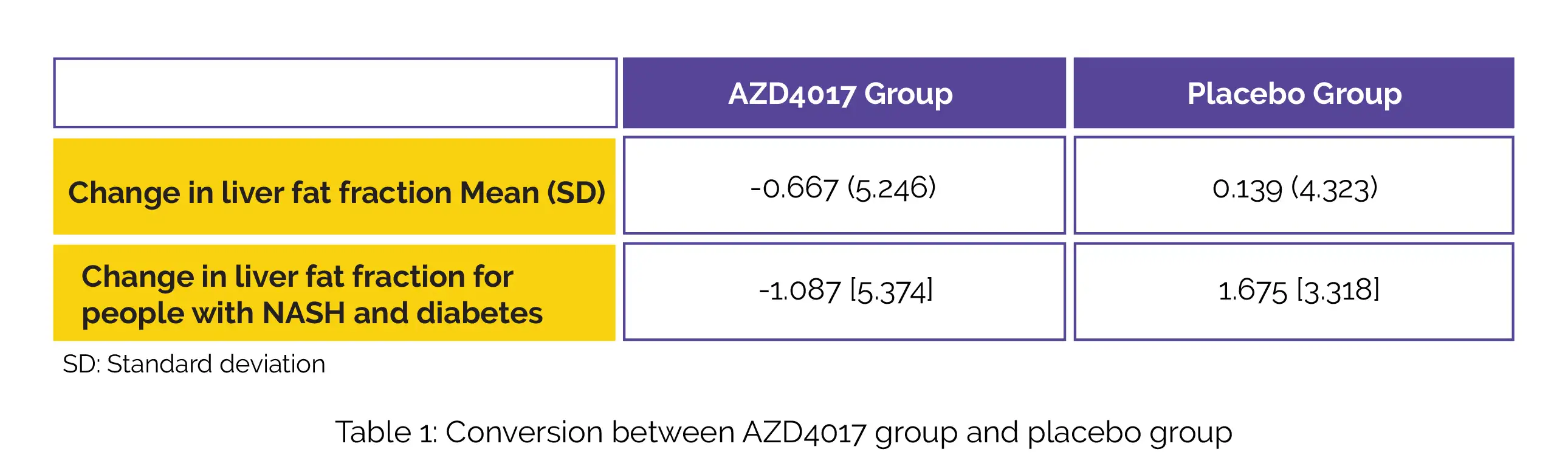
The between-group differences in the mean alteration from baseline to week twelve in liver fat fraction and conversion of 13C cortisone to 13C cortisol in the liver were the major outcomes ascertained. Overall, 93 subjects were randomized; 85 subjects completed therapy. The mean alteration in the liver fat fraction in the AZD4017 and placebo groups is shown in Table 1. For people having NASH and type 2 diabetes, remarkable improvements in mean alteration in the liver fat fraction was noted in the AZD4017 group when compared to the placebo group (Table 1).
In the AZD4017 group, the conversion of 13C cortisone to 13C cortisol was inhibited in all the subjects. This indicates that the likely mechanism of action of AZD4017 is suppression of hepatic 11β-HSD1 activity.
Regarding alteration in fibrosis, levels of liver enzymes or lipids, insulin sensitivity, and weight, no profound between-group differences were witnessed. Thus, an appropriate therapeutic agent to treat NASH and NAFLD could be a combination agent including a 11β-HSD1 inhibitor drug that targets the liver /adipose tissue. Also, AZD4017 might offer some metabolic benefits to people with type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Inhibition of 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 with AZD4017 in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II study
Yogesh Yadav et al.
Comments (0)